What is An FHA Loan?
An FHA loan is a mortgage option, approved by lenders and insured by the FHA (Federal Housing Administration). The borrowers get a smaller down payment and at any income level, they can still be eligible for this loan.
FHA does not provide home loans but they instead guarantee the lenders a repayment in case you default on the loan. The guarantee is what makes mortgage companies and banks work with a borrower who under normal circumstances, would not qualify for conventional home loans.
FHA Loans for First Time Homebuyers
A majority of Americans believe that FHA mortgage loans are for individuals with bad credit or those who have low income. However, this is not true. This is the most popular home loan products that is used in the United States.
Approximately 40% of home loans are FHA loans. The flexibility of their qualifying guidelines and their low down payment makes them very popular.
FHA Loans And Low-Income Buyers
Most borrowers will easily get approved for these mortgage loans since FHA loans have a more flexible debt to income ratio as compared to the traditional mortgages.
FHA Loan For A First Home Buyer With A Bad Credit
It is very reasonable for a first-time home buyer who has a bad credit to consider getting an FHA loan. With a credit score just 500 you can be eligible for this particular loan. Having a poor credit, however, will mean that you will have to pay bigger interests and higher monthly payments.
In this article, we shall look at a few basic things that you need to know about FHA home loans.

Prequalification for An FHA Home Loan
- Bankruptcy. Two years should have elapsed since you or/and your spouse bankruptcy charges were discharged. Nonetheless, lenders will require different waiting periods depending on the type of loan that you are borrowing.
- Short sale. You will qualify for an FHA loan after three years from your short sale. If you had no late payments for your mortgage for the previous twelve months, there will be no waiting period required.
- Foreclosure. You must have resolved your foreclosure for not less than three years since the resolution date, and you should not have had any late payments.
- A steady employment. You should have at least a two years employment history.
- You should be of legal age, be a legal U.S citizen and have a valid social security number.
With that being said there are other FHA loan requirements that you must meet:
- Minimum Down Payment Requirements
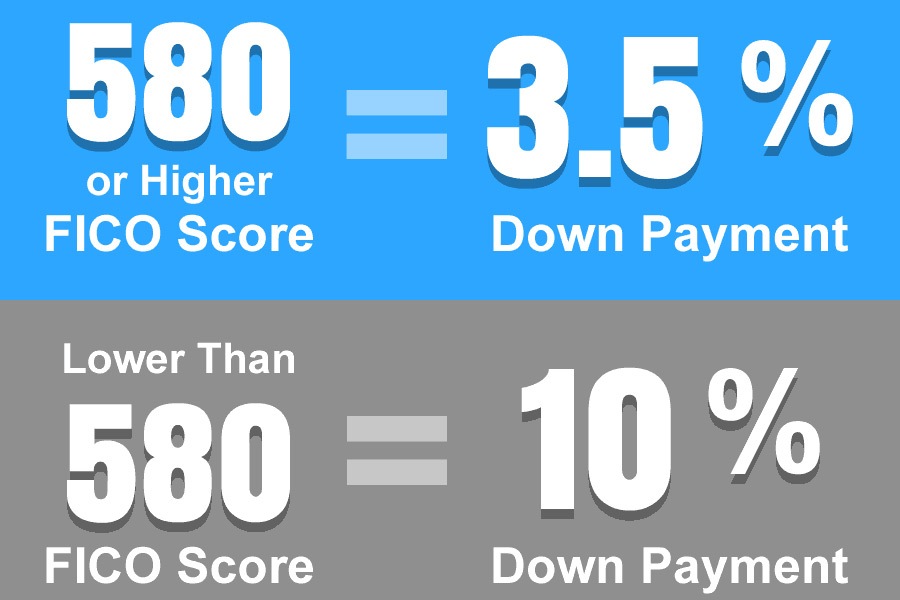
A minimum of 3.5% is required as a down payment when purchasing the property. You can make the down payment using your savings, a government grant or even a financial gift from your family or friend.
You must also have a credit score of 580 or higher. If your credit score ranges from 500 to 579, you will qualify for a loan to value ratio of a maximum of 90% and a 10% down payment will be required from you.
- Credit Score(FICO) Requirements
For an FHA loan, the down payment will entirely depend on your credit score. As mentioned above, to take full advantage of the 3.5% down payment, you will need a minimum credit score of 580. A 10% down payment will only be required from borrowers whose credit score ranges from between 500 and 579.
FHA home loan does not require an exceptional credit score of 800. With little blemishes of foreclosure or bankruptcy, you can still qualify. The minimum credit score for bad debt is 500.
- Debt Ratio Requirements
The minimum debt- to- income ratio according to FHA is 56.9% for borrowers with a credit score of 620 or higher. The United States Department of Housing and Urban Development or the HUD, however, prefers the FHA borrowers to have a debt to income ratio that does not exceed 43%. This simply means that the total monthly expenses including the mortgage payment should not use more than 43% of your monthly income. There is an exception for individuals who have a history of making similar payments successfully and/or those with significant cash reserves.
- Paperwork Requirements
During the mortgage documentation process, you are required to verify your assets, income and debts. This rule has become more important as a result of the current government lending standards. In 2014, the (ATR) Ability To Repay rule took effect and nowadays, lenders can obtain various financial documents to verify that a borrower has the ability to repay the debt. This rule applies to FHA mortgage loans as well, and the lender can ask for W-2 forms, bank statements or tax returns.
- FHA Closing Costs
Just like all other home loans, FHA comes with closing costs. The fee will include a title insurance, home appraisals and origination fees. Depending on your lender, FHA closing cost can range from between 2% and 5% of the purchase cost.
Before you decide to settle on your preferred mortgage, compare loan offers from different FHA lenders to ensure you get the lowest fee and the most competitive rates.
- Mortgage Insurance
Mortgage insurance is a must for borrowers who have put down less than 20% as a down payment. This insures lenders in case a borrower defaults on his/her mortgage. The two mortgage insurance premiums required by all FHA loans include;
- Upfront premium. 1.75% of the total loan is paid when the borrower gets the mortgage. The premium will be rolled into the borrower’s financial loan.
- Annual premium. It will be 0.45% to 1.05% depending on the loan-to-value ratio (LTV) and loan term. The premium amount is usually divided into twelve and paid on a monthly basis.
When a borrower is given $150,000 for instance, the upfront will $2,625 and the annual premium will range from $675 to $1,575.
- The Lender That You Choose Should Be Approved By FHA
As mentioned above, FHA is not a creditor. Borrowers can only get their home loans from lenders who have been approved by FHA. Different lenders will have different fees, costs and rates even for a similar loan.
You can get an FHA loan from credit unions, banks or independent lenders. The services, documentation standers and costs will vary among the different mortgage brokers and lenders, therefore, you should take your time and compare the different available options so that you get the best deal.
History of the FHA loan program
The US Congress introduced the FHA firstly in 1934 when the country was struggling with the Great Depression. During this period, approximately 2 million workers lost their jobs, making it challenging for them to get mortgages. The terms of mortgage loans were limited to only 50% of the market value of the property and the repayment schedule lasted from 3 to 5 years with a balloon payment in the end.
In the 1940s, the FHA programs financed military housing as well as properties for returning veterans after wars. During the 50s, 60s, and 70s, it facilitated the generation of many privately-owned apartment units for lower income, handicapped, and elderly people in the United States. In 1965, this program officially became an important part of the HUD or Housing and Urban Development. When energy expenses and increased inflation threatened the development of private apartment projects during the 70s, the emergency financing of the FHA helped many cash-strapped properties survive.
The FHA experienced a stable period of reducing home prices and helped many potential homebuyers receive the necessary loans when the depression caused private insurers to withdraw from oil-producing countries during the 80s. Until 2001, the rate of homeownership in the country had increased up to 68 percent, which was the highest one of all time.
Between 2008 and 2013 when the financial crisis occurred, FHA played an essential part in supporting the housing market by providing access to a different mortgage when other financing sources were limited as well as the capital market was being seized up.
These days, FHA has more than 8 million single-family mortgages with active insurances, 3700 mortgages for residential facilities, 100 hospital facilities mortgage, as well as approximately 12,000 multifamily properties mortgages. The total unpaid balance is more than $1.3 trillion.
Types of FHA loans
FHA loans can be divided into many different types. These include:
– Traditional mortgage: This is the most common type of FHA loan which provides access to typical home loans for those people who are experiencing trouble in financing their new house.
– 203K improvement loans: This type takes into account the expenses of several renovations and repairs. It will enable the participants to borrow for a home improvement or purchase. This can be helpful when you do not have plenty of cash money available after the down payment.
– HECM program: HECM stands for Home Equity Conversion Mortgage, which is a reverse mortgage to help older people who are more than 62 years old to convert their equity in houses into cash but can still retain the title to their house. They would choose the method of withdrawing their funds, typically between a line of credit and a fixed amount each month (a combination is also possible).
– Energy-efficient mortgage: As the name implies, this type of FHA loan aims at any repair or renovation that would improve energy efficiency and reduce monthly utility bills. These might include wind energy or solar system, new insulation, or similar ideas. The main thing to know is that energy-efficient houses often have much lower operating expenses, which would eventually reduce the bills and allow for more income for your mortgage payments.
– Section 245(a): In this program, participants must show that they would increase their incomes in the future. Under the policies of this type, a GPM or a graduated payment mortgage with lower monthly payments in the beginning will increase gradually. In addition, the GEM or growing equity mortgage with scheduled raises in monthly payments will lead to shorter terms of the loan.
Limits of the FHA loan
A disadvantage of the FHA loans is that the program set some particular limits on the amount that the applicants could borrow. These loan limits can vary greatly, depending on the county and state that you are living. In general, low-cost regions often have a lower limit than the FHA loans, while high-cost regions often have a higher limit. In addition, there is a loan limit for the whole country: the floor or minimum limit is around $314,000 and the ceiling or maximum limit is around $726,000.
There are a few exceptions in several states and territories. These include the U.S. Virgin Islands, Guam, Hawaii, and Alaska. The costs of construction in these areas are extremely high, which leads to even higher limits. In other states, the limit is often set around 115 percent of the median house price, which will be decided by the United States DHU. In addition, the limits can be different based on the number of units.
Relief for FHA loans
One of the most important advantages of FHA loans is the relief. This means that when you are accepted for a loan with the guarantee of the FHA, you might be valid for loan relief in case of an eligible financial trouble. For instance, if you lose a large amount of money or have a considerable increase in your living costs, the difficulty in making monthly payments for the mortgage can be a good reason for FHA loan relief.
The HAMP program of FHA could reduce the monthly mortgage payments permanently to a more affordable level to help participants avoid foreclosure. To be eligible for this program, an applicant has to go through a trial payment period in which he or she needs to make 3 scheduled payments timely at the modified and lower amount.








Leave a Reply